
Classification of phase demodulation techniques
A first classification is based on the distinction between global and local methods. A local method computes the optical phase at a single point by using the successive values of the signal at this point, or by using an ensemble of values in a group of neighboring points. A global method will give the optical phase at all the points where the fringe pattern was registered. There is therefore a major difference between the two approaches: for the local method, the values of
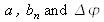 stay constant within each calculation cell, whereas for the global method for which the calculation cell encompasses the full fringe pattern, the phase
stay constant within each calculation cell, whereas for the global method for which the calculation cell encompasses the full fringe pattern, the phase
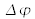 varies in the field, and its evaluation depends on the ability to suppress the variations of a, bn by isolating their contributions.
varies in the field, and its evaluation depends on the ability to suppress the variations of a, bn by isolating their contributions.
Another classification can be based on the distinction between temporal and spatial methods. In the first case, the data used for phase determination are obtained at various time intervals, whereas in the second case all the data is acquired simultaneously.
In this lesson, we decided to classify the methods depending whether they involve a spatial carrier or not. Indeed, the methods based on a spatial carrier utilize the same spatial domain to represent the image (the pixels), contrary to the other methods for which each pixel is examined independently from the others and at different time points, necessitating the acquisition of several fringe patterns taken at various time points.
The limitations of the spatial carrier technique thus appear in the dynamic range, and therefore in the spatial variations of the phase that are tolerable for this method. These limitations are related to the spectral overlapping effects, and can be expressed as a fraction of the carrier frequency, for which the ultimate limitation is the pixel density compared with the fringe density. However, these methods require the acquisition of only one fringe pattern to estimate the phase and are therefore well adapted to dynamic phenomenons: they can be described as real time methods.
According to this criterion, the methods will be classified as follows :
-
Phase demodulation without spatial carrier
-
temporal phase shifting
-
phase stepping
-
spatial phase shifting
-
-
Phase demodulation with spatial carrier
-
Fourier transform demodulation
-
phase shifting with spatial carrier
-
spatial lock-in demodulation
-
Each of these methods will be presented later on.