
Reconstruction by convolution
The hologram in figure 22 was used to illustrate reconstruction by convolution.
The pixel matrix covers an area of
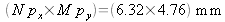 . The object has a diameter of 25mm; the number of spectral scans is therefore
. The object has a diameter of 25mm; the number of spectral scans is therefore
 and the reconstructed field made by the attachment of the different zones would contain
and the reconstructed field made by the attachment of the different zones would contain
 pixels, which is a considerable size! The sampling pitch of the reconstructed field is the same as that for the sensor
pixels, which is a considerable size! The sampling pitch of the reconstructed field is the same as that for the sensor
 .
.
The spectral contents of the hologram is given by its Fourier transform. Taking into account the modelling we saw in the course for the plane reference wave, we get :
Where
 is the Fourier transform of the wave diffracted by the object and
is the Fourier transform of the wave diffracted by the object and
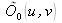 is the Fourier transform of
is the Fourier transform of
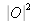 . The spectrum is therefore trimodal and the spectral content which corresponds to the object is located at the frequential coordinates
. The spectrum is therefore trimodal and the spectral content which corresponds to the object is located at the frequential coordinates
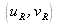 .The filter bank used in the reconstruction of the object must therefore scan the spectral zone which surrounds the average frequency
.The filter bank used in the reconstruction of the object must therefore scan the spectral zone which surrounds the average frequency
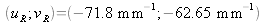 .
.
Figure 27 shows the hologram's spectrum.
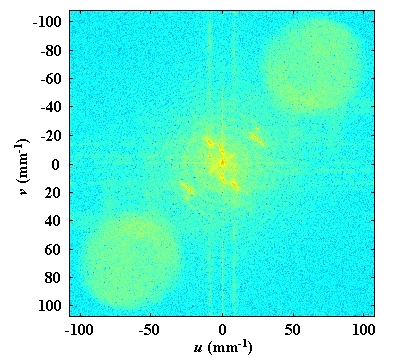
Figure 28 shows the spectrum of the exact impulse response of the free space which is used in reconstruction by convolution.
The bandwidth of the transfer function of the free space is clearly insufficient in order to cover the useful bandwidth of the hologram in a single operation.
Figure 29 shows the +1-order reconstructed by convolution by applying the algorithm shown in figure 18.

Figure 30 shows a comparison between the object reconstructed by 4096 point zero-padding and the object reconstructed by convolution.

We can see that the convolution gives a result which corresponds to that given by zero-padding with a format which does not match the number of points required for FFT algorithms (in 2n).
The convolution method is highly appropriate for use with small objects but on the other hand is not recommended for objects which are larger than the pixel matrix because the final image contains a considerable number of points which increase the necessary calculation time and makes any digital processing highly delicate.