Fundamentals of geometrical optics

Calculating the full light field
Figure EC2 shows that L1 is pupil and L2 secondary stop because the farthest ray for one point on the axis goes through the side of L1. EC3 shows a ray beam arising from the edge of the full light field.
The farthest ray beam goes through the pupil side and the edge of the secondary stop. It cuts the intermediate field situated in the focal plane of L1 to 10 mm from the axis.
The magnification of the conjugation
 of L2 being 3, the full light field edge is at 30 mm from the axis. Therefore the total dimension of the full light field is 60 mm.
of L2 being 3, the full light field edge is at 30 mm from the axis. Therefore the total dimension of the full light field is 60 mm.
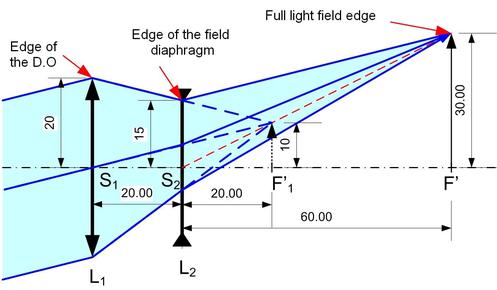
Figure EC 3
[zoom...]