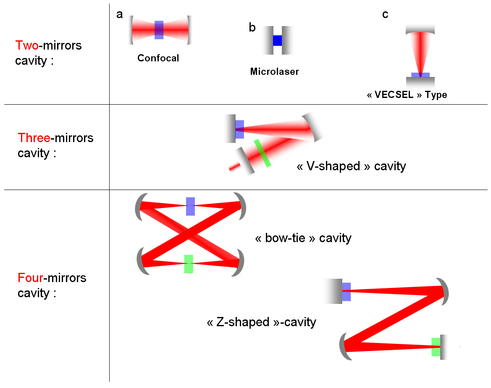
Other resonators
The detailed calculation was done for the two-mirrors cavity. In numerous cases, this geometry is not the best choice to get the desired laser.
Three-mirrors cavities (see figure 17) are widespread : it is possible for example with such resonators to benefit from a collimated beam in one branch of the cavity, which is very useful when one wants to add optical elements inside the resonator (Lyot filter, polarizing optics...)
It could also be desirable to have two waists in the resonators, with different sizes : one is used to put the amplifying medium, the other for example for a saturable absorber (Q-switch laser operation) or a non-linear crystal (frequency mixing). 4-mirrors geometries such as the one depicted on figure 17 are then a good choice.
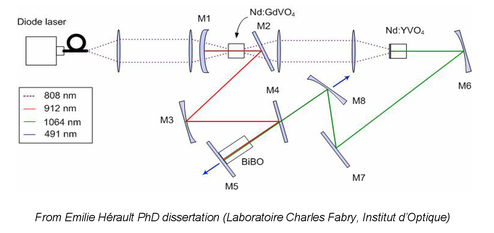
Finally, one can imagine intricate cavities with several laser and/or non-linear crystals to mix several wavelengths ( figure 18 is a beautiful example ) : the only limit is in laserist's minds...